Magnitude Math Definition
The magnitude of a vector is its length ignoring direction.
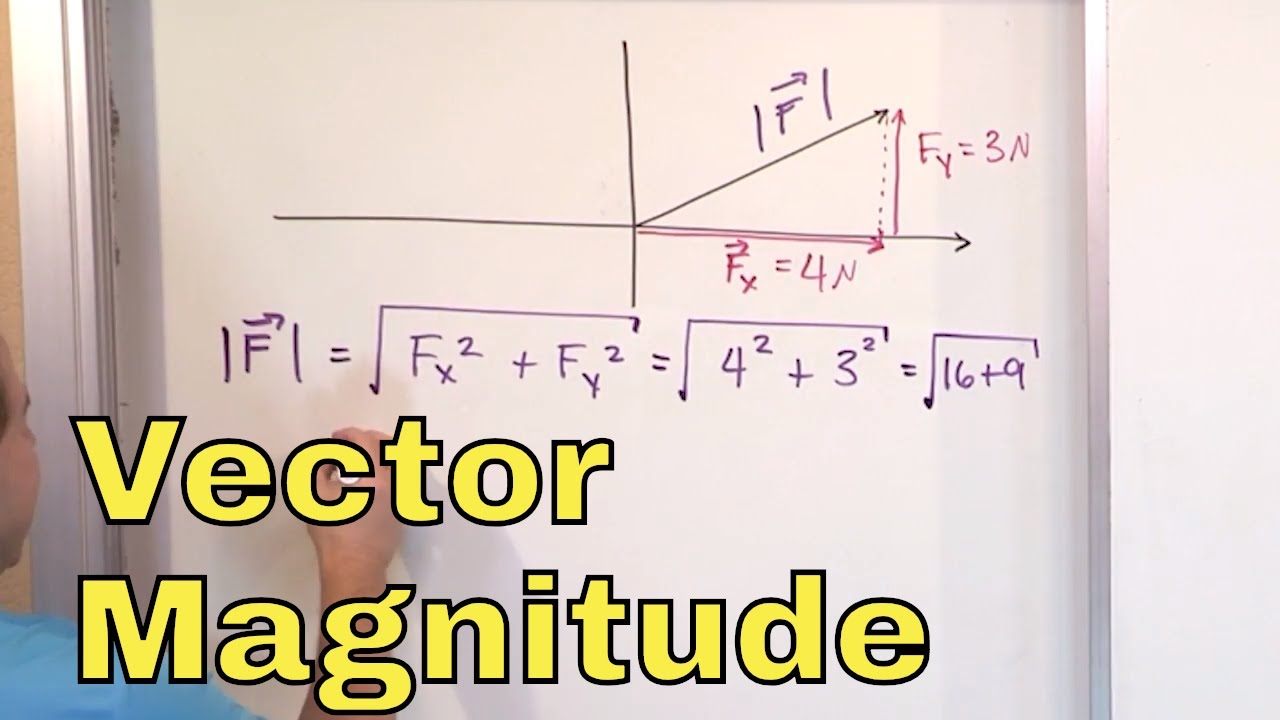
Magnitude math definition. Formulas for the magnitude of vectors in two and three dimensions in terms of their coordinates are derived in this page. Orders of magnitude are generally used to make very approximate comparisons. In physics the strength of a force is usually expressed by its magnitude. For numbers such as 1 2 3 and so on the magnitude is simply the number itself.
The magnitude of the vector vc a is denoted as vc a. Although a vector has magnitude and direction it does not have position. Displaystyle n the number is first expressed in the following form. In math this means how far away the math term is from zero.
See the introduction to vectors for more about the magnitude of a vector. In mathematics magnitude or size of a mathematical object is a property which determines whether the object is larger or smaller than other objects of the same kind. It is typically represented symbolically by an arrow in the proper direction whose length is proportional to the magnitude of the vector. Magnitude is the size of any mathematical object which can be compared with its related set of objects.
If two numbers differ by one order of magnitude one is about ten times larger than the other. The magnitude of a number also called its absolute value is its distance from zero so. Magnitude definition is great size or extent. A kilometer 1000 meters is three orders of magnitude greater than a meter.
More formally an object s magnitude is the displayed result of an ordering or ranking of the class of objects to which it belongs. For a two dimensional vector vc a a 1 a 2 the formula for its magnitude is begin gather vc a sqrt a 1 2 a 2 2. The size of something. Can also be used to mean very much bigger or smaller.
It is mainly used while doing scientific notation. The order of magnitude of 170 is 2 because it is around 100 in size. Displaystyle n a times 10 b where. A vector is not altered if it is.
How to use magnitude in a sentence. The order of magnitude of 12 is 1 because it is around 10 in size. Play with a vector below. Generally the order of magnitude of a number is the smallest power of 10 used to represent that number.
The magnitude of a vector is the length of the vector. If they differ by two orders of magnitude they differ by a factor of about 100. N a 10 b. The size of an object depicts its order in the set of objects.
A quantity that has both magnitude and direction. To work out the order of magnitude of a number.


















