Magnitude Of A Vector Notation Math
A vector representing a unit vector is usually also boldface although it will have a carat above it to indicate the unit nature of the variable.
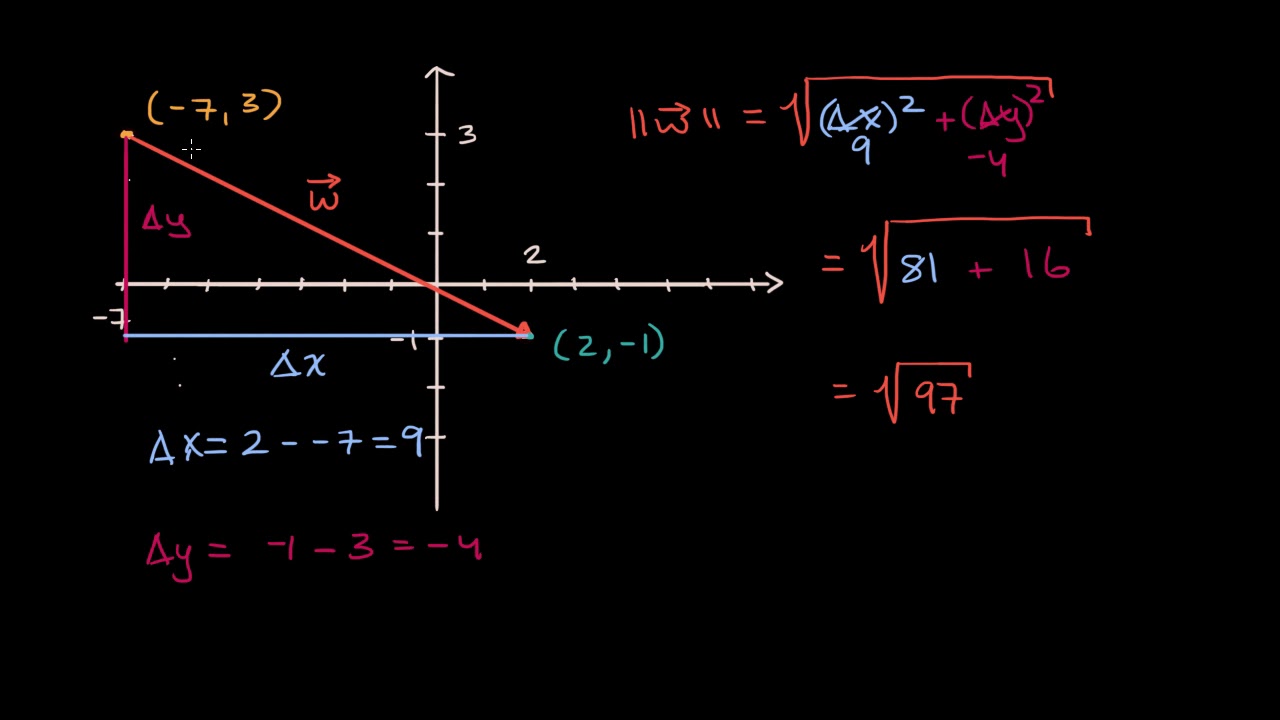
Magnitude of a vector notation math. Logarithmic magnitudes can be negative and cannot be added or subtracted meaningfully since the relationship is non linear. Forms notation and formulas a scalar is a mathematical quantity with magnitude only mass pressure or speed are good examples of scalars. A vector quantity has magnitude and direction. Be careful to distinguish vector notation left langle 2 5 right rangle from the notation we use to represent coordinates of points left 2 5 right.
Begingroup it is a constant struggle in math. Displacement velocity momentum force and acceleration are all vector quantities. Ask question asked 4 years 3 months ago. A unit vector is a vector that has a magnitude of one.
Share cite. So don t mix the notations up. A vector quantity has magnitude and direction. U i wonder because on ap physics formula sheets sometimes the magnitude of a vector is clearly denoted while other times the quantity is written as scalar with no vector arrow.
In a pseudo euclidean space the magnitude of a vector is the value of the quadratic form for that vector. The vector denotes a magnitude and a direction of a quantity while the point denotes a location in space. Examples include the loudness of a sound measured in decibels the brightness of a star and the richter scale of earthquake intensity. Displaystyle r 5 theta pi over 9 h 3.
The unit vector x when written with a carat is generally read as x hat because the carat looks kind of like a hat on the variable. About the book author mark zegarelli a math tutor and writer with 25 years of professional experience delights in making technical information crystal clear and fun for average readers. A three dimensional vector the magnitude of whose projection onto the xy plane is 5 units whose angle from the positive x axis is π 9 radians 20 and whose height from the xy plane is 3 units can be specified in any of the following forms. When comparing magnitudes a logarithmic scale is often used.
The magnitude of a vector is the distance from the origin of a graph to its tip just as the absolute value of a number is the distance from 0 on a number line to that number. Two dimensional vectors can be represented in three ways.

















