Tangent Ratio Definition Math
In a right triangle abc the tangent of α tan α is defined as the ratio betwween the side opposite to angle α and the side adjacent to the angle α.
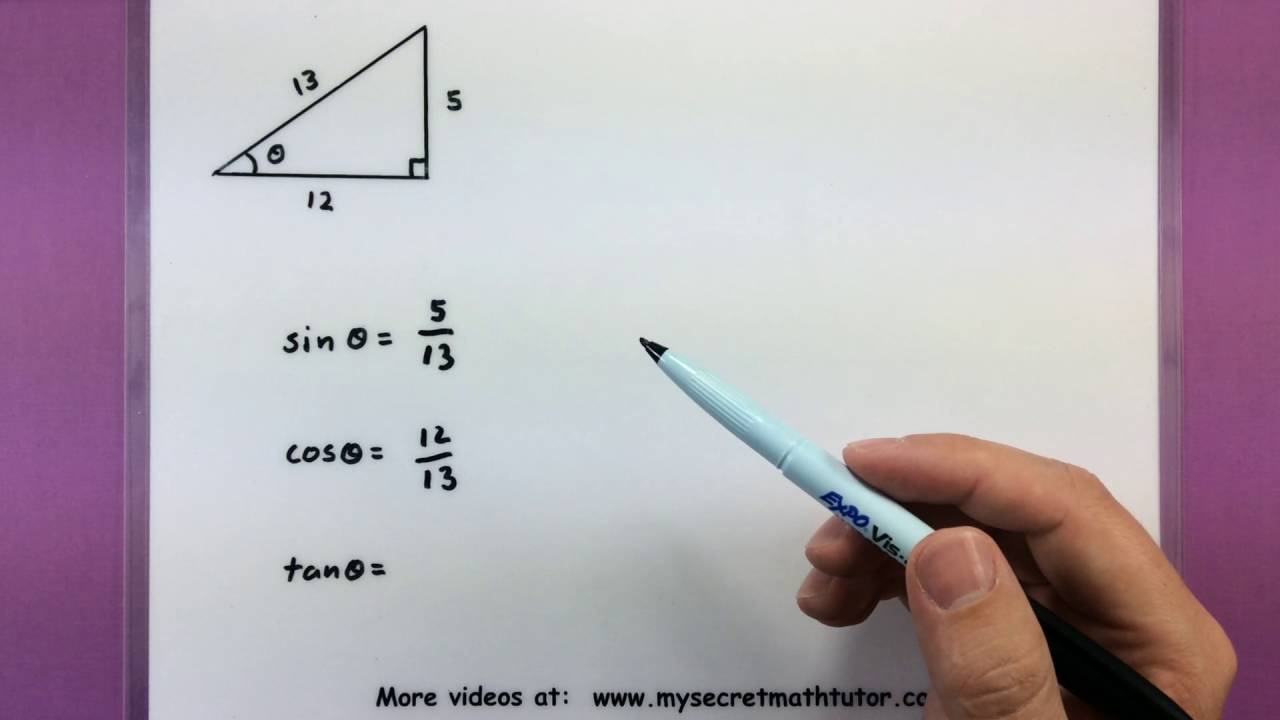
Tangent ratio definition math. The ratio of the length of the opposite side of an angle divided by the length of the adjacent side in a right triangle is called the tangent of the angle. For a given angle θ each ratio stays the same no matter how big or small the triangle is. Divide the length of one side by another side. The full 30 minute episode is available on discovery channel dvd and is well worth watching during a math class on triginometry.
Right triangle definition for a right triangle with one acute angle θ the tangent value of this angle is defined to be the ratio of the opposite side length to the adjacent side length. A 3 b 4 tan α a b 3 4 0 75. In short we can use the symbol tan instead of tangent and write tan 45 degrees 1. Trig worksheet 3.
Do any of the following worksheets for practice with tangent ratio questions. It is very commonly abbreviated as tan. This function can be used to determine the length of a side of a triangle when given at least one side of the triangle and one of the acute angles. Tangent is a trigonometric ratio comparing two sides of a right triangle.
The right angled triangle definition of trigonometric functions is most often how they are introduced followed by their definitions in terms of the unit circle. We then say that tangent of 45 degrees is equal to 1. This specific ratio also called trigonometric ratio is called tangent ratio. Sine cosine and tangent often shortened to sin cos and tan are each a ratio of sides of a right angled triangle.
The tangent ratio is the value received when the length of the side opposite of angle theta is divided by the length of the side adjacent to angle theta.

















